Gas leaks are invisible threats that can lead to catastrophic consequences in industrial environments. From toxic exposure and fire hazards to regulatory violations and production downtime, undetected gas leaks pose serious risks to people, assets, and the environment. Implementing a reliable gas leak detection system is critical for maintaining safety, ensuring compliance, and improving operational efficiency.
Whether in a chemical plant, power facility, refinery, or food processing unit, understanding how gas detection works and where it is most needed can prevent major incidents. With advances in sensing technology and integrated monitoring systems, industries now have more tools than ever to detect, measure, and respond to leaks in real time.
In this blog, we explore the core principles of gas-leak detection—what it is, why it’s essential, the technologies behind it, and how various industries apply it to ensure safer operations and better outcomes.
Gas leak detection refers to the process of identifying the accidental release of gases into the atmosphere, particularly hazardous ones that pose safety, health, or environmental risks. These gases may be flammable, toxic, corrosive, or asphyxiating. Common examples include methane (CH4), Hydrogen sulfide (H2S), carbon monoxide (CO), ammonia (NH3), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
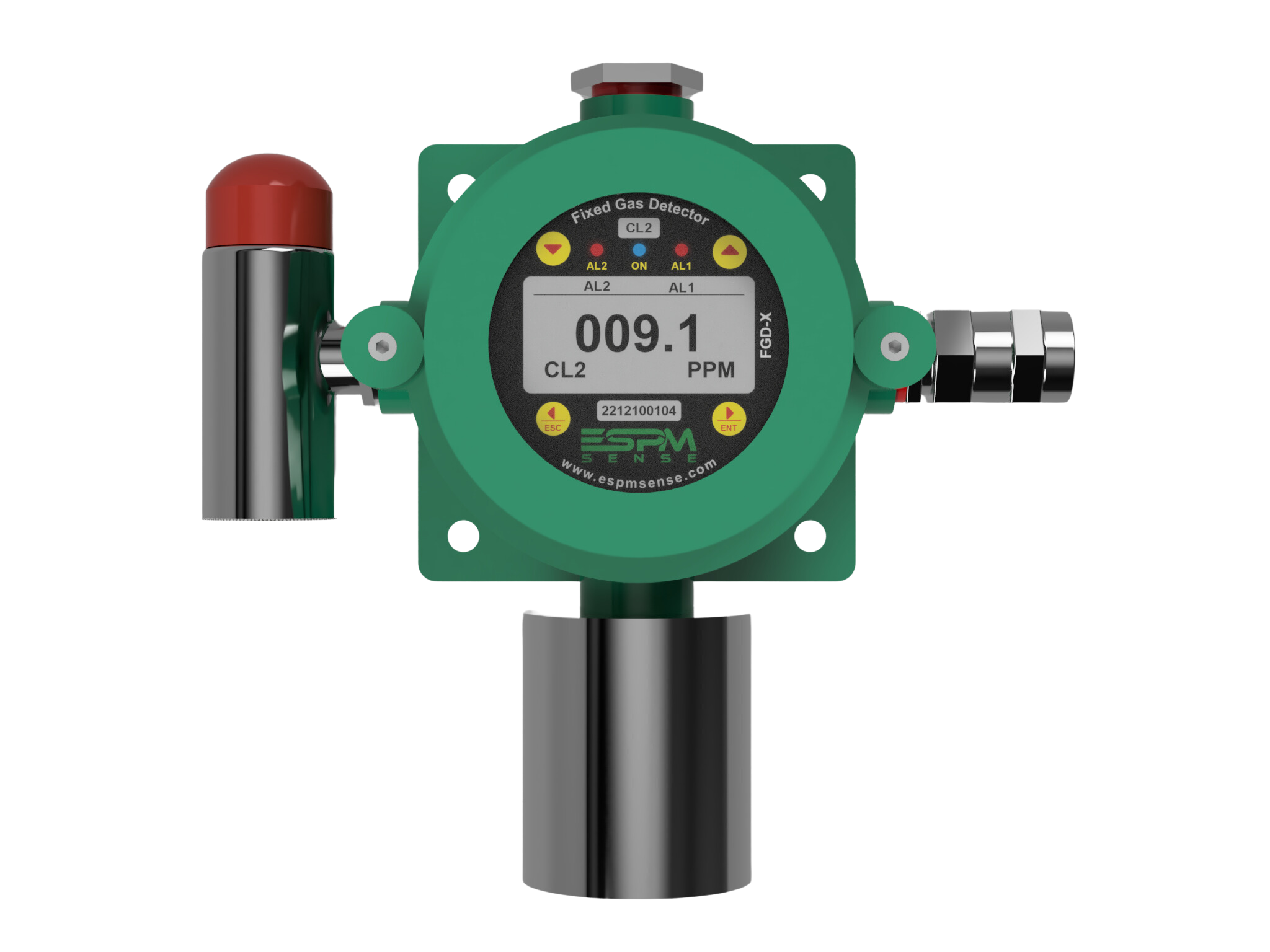
Gas detection systems use specialized sensors to monitor the presence and concentration of these gases in specific areas. When gas levels exceed preset thresholds, alarms are triggered, and safety protocols are activated. This allows for immediate response, helping to prevent injuries, explosions, or shutdowns.
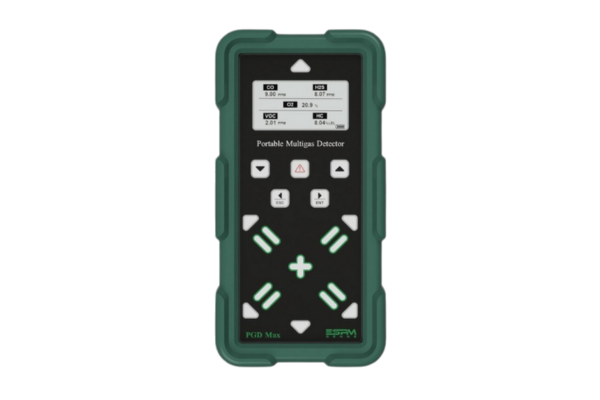
Key components of a gas detection system include the sensor (which detects the gas), a transmitter (which processes the signal), and an alarm or controller system (which notifies personnel or activates emergency responses). Depending on the application, systems may be fixed (stationary units monitoring key locations) or portable (handheld devices for mobility and spot checks).
By continuously monitoring for leaks, these systems offer early warning and allow industries to maintain safe, compliant, and efficient operations.